 | ||
| 26th June 2025 | view in browser | ||
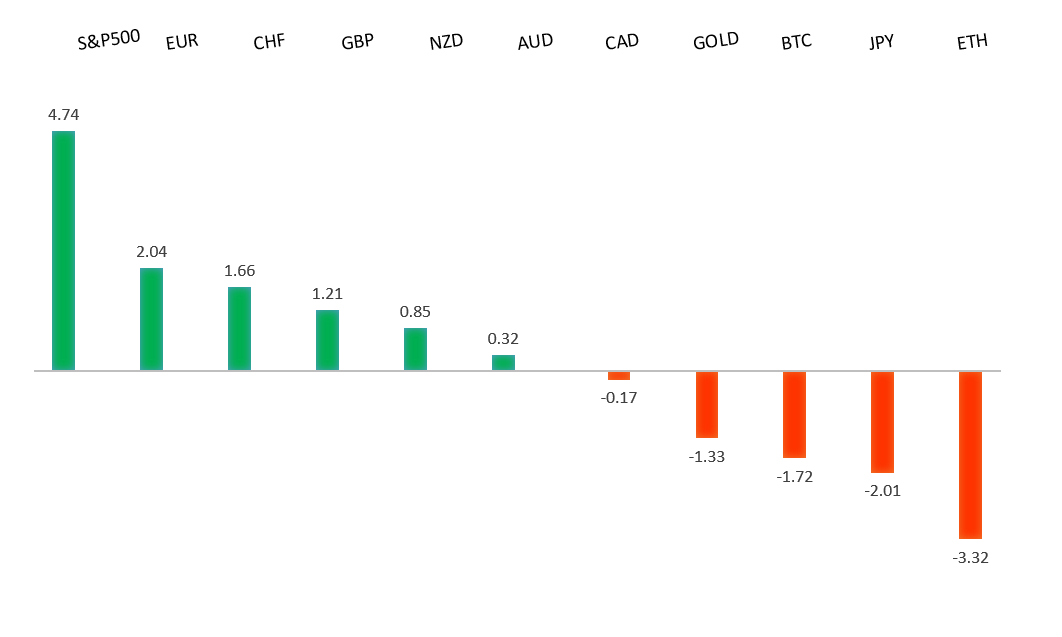
| Euro extends to another yearly high | ||
| Reports from the Wall Street Journal have opened more downside pressure on the Buck, while fueling fresh 2025 highs in currencies like the Euro and Pound. These reports say President Trump is frustrated with the Federal Reserve’s slow approach to cutting interest rates. | ||
| Performance chart 30day v. USD (%) | ||
 | ||
| Technical & fundamental highlights | ||
| EURUSD: technical overview | ||
| The Euro has finally broken out from a multi-month consolidation off a critical longer-term low. This latest push through the 2023 high lends further support to the case for a meaningful bottom, setting the stage for a bullish structural shift and the next major upside extension targeting the 2021 high at 1.2350. Setbacks should be exceptionally well supported below 1.1000. | ||
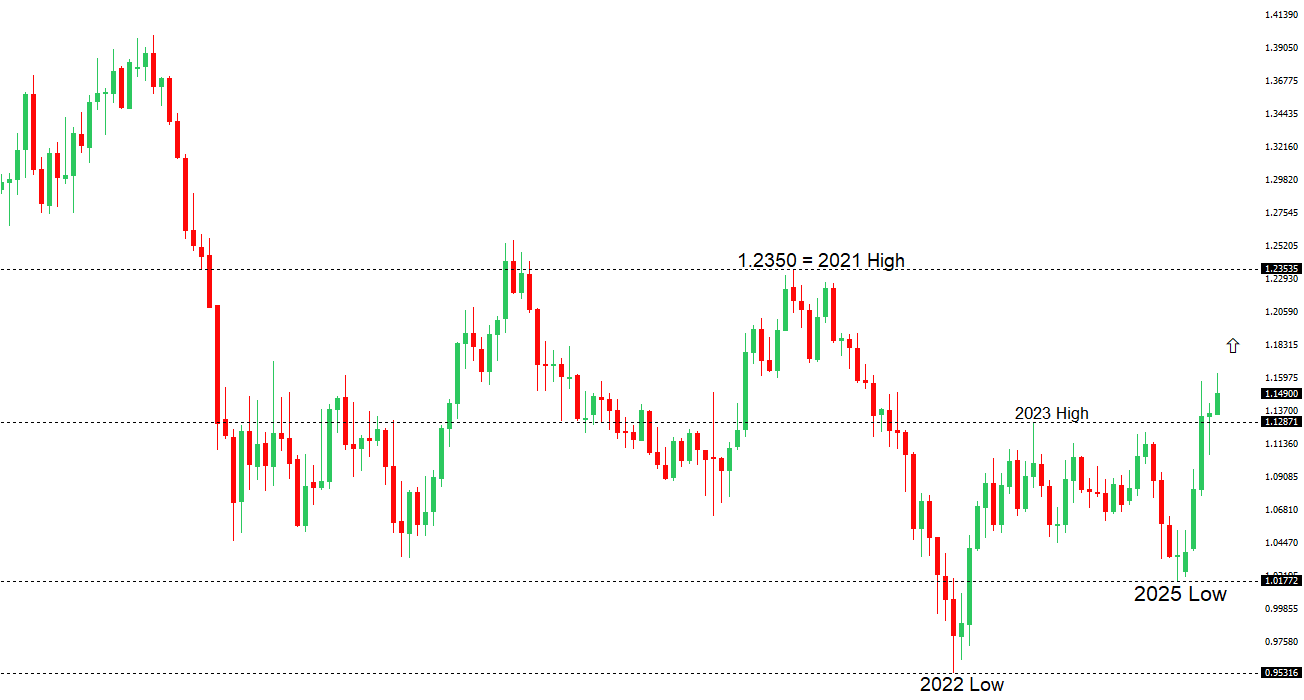 | ||
| R2 1.1718 - 26 June/2025 high - Medium R1 1.1700 - Figure - Medium S1 1.1573 - 24 June low - Medium S2 1.1446 - 19 June low - Strong | ||
| EURUSD: fundamental overview | ||
| The euro has surpassed the key 1.17 level, with bank strategists forecasting a rise to 1.20 or even 1.23 by year-end, driven by faster U.S. interest rate declines compared to other G10 nations. NATO leaders have agreed to increase defense spending to 5% of GDP by 2035, a historic shift from 2%, prompted by Russian threats, with Germany aiming to lead Europe’s military buildup. This deal, a win for both President Trump and European leaders, signals greater European unity and strategic autonomy, potentially boosting the euro’s value and reserve currency status, though concerns remain about crowding out private investment and rising public debt. Germany’s Gfk Consumer Confidence Index is expected to improve slightly to -19.2 in July from -19.9, reflecting fragile economic optimism that could be disrupted by trade or geopolitical tensions. | ||
| USDJPY: technical overview | ||
| There are signs of a meaningful top in place after the market put in a multi-year high in 2024. At this point, the door is now open for a deeper setback below the 2024 low at 139.58 over the coming weeks, exposing a retest of the 2023 low. Rallies should be well capped below 150.00. | ||
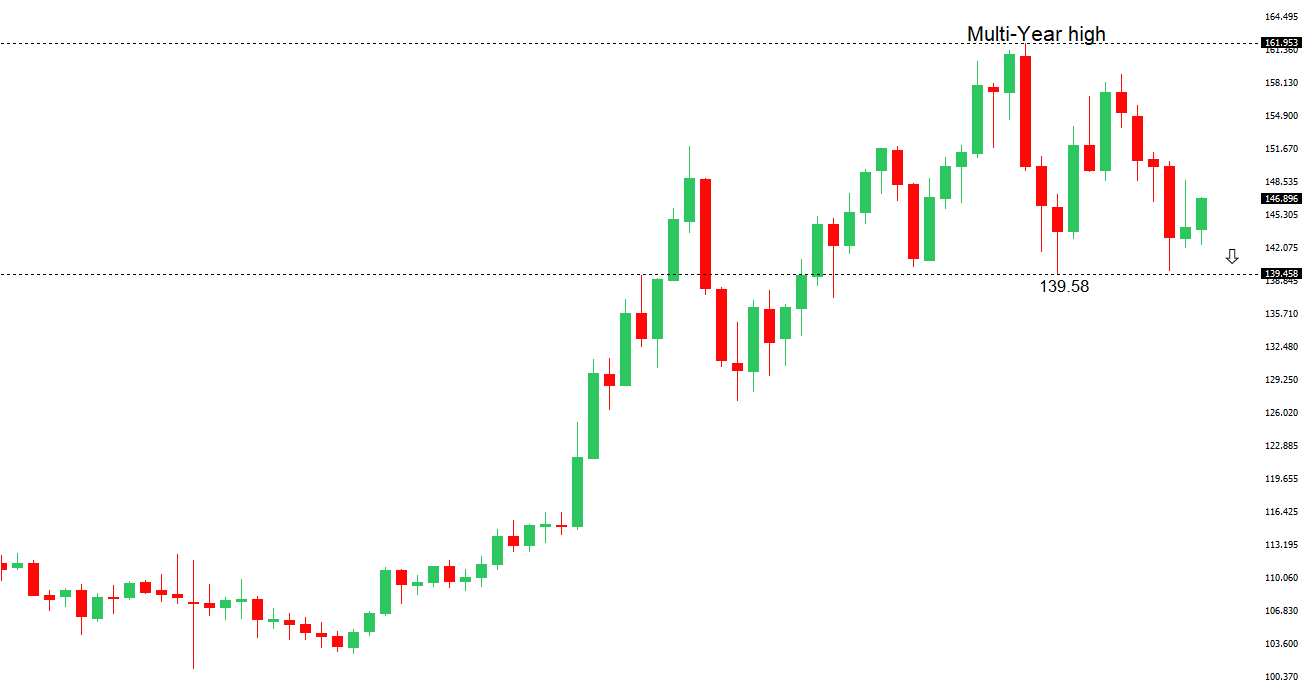 | ||
| R2 148.65 - 12 May high - Medium R1 148.03 - 23 June high - Medium S1 144.32 - 18 June low - Medium S2 142.79 - 13 June low - Medium | ||
| USDJPY: fundamental overview | ||
| Bank of Japan Board member Naoki Tamura indicated that the central bank might need to raise interest rates decisively if inflation risks increase, potentially achieving price stability sooner than anticipated due to stronger-than-expected inflation data. Despite these risks, the BOJ plans to maintain its current monetary policy due to economic uncertainties, including U.S. tariffs and Middle East tensions. Tamura noted a low but non-zero chance of a rate hike during ongoing U.S.-Japan trade talks, which focus on U.S. tariffs on Japanese automobiles, with Japan emphasizing its significant investments and job creation in the U.S. A favorable trade deal could strengthen the Yen and support BOJ’s policy normalization, while upcoming data, including a steady 2.5% jobless rate and a slightly softer Tokyo CPI of 3.3%, reflects a tight labor market and persistent inflationary pressures, keeping the BOJ on track for monetary normalization. | ||
| AUDUSD: technical overview | ||
| There are signs of the potential formation of a longer-term base with the market trading down into a meaningful longer-term support zone. Only a monthly close below 0.5500 would give reason for rethink. A monthly close back above 0.7000 will take the big picture pressure off the downside and strengthen case for a bottom. | ||
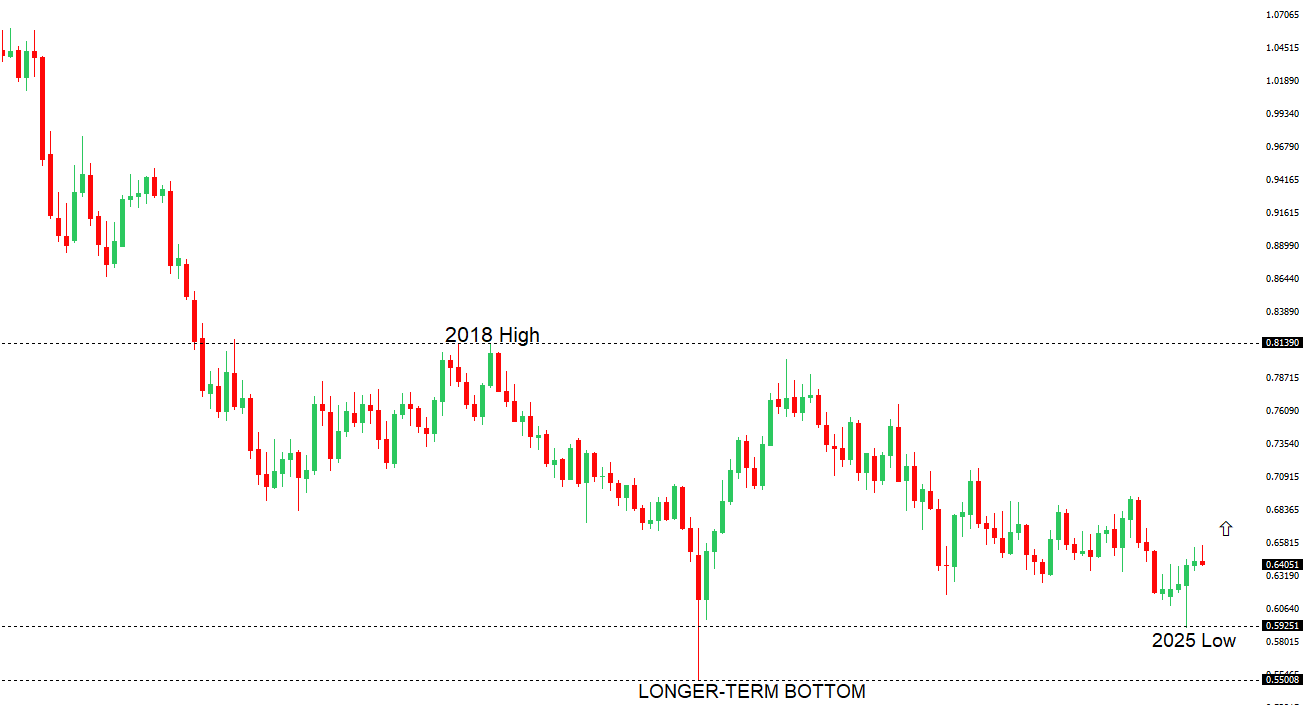 | ||
| R2 0.6553 - 16 June/2025 high - Strong R1 0.6537 - 26 June high - Medium S1 0.6373 - 23 June low - Medium S1 0.6344 - 24 April low - Strong | ||
| AUDUSD: fundamental overview | ||
| Australia’s economy is projected to grow by 1.7% in 2025, 2.3% in 2026, and 2.5% in 2027, according to a Bloomberg survey of economists. Inflation is expected to remain steady at 2.5% in 2025 and 2.7% in 2026, with May 2025 inflation at 2.1%, below the consensus of 2.3%. The Reserve Bank of Australia’s interest rate is forecasted to reach 3.60% by Q3 2025, and upcoming retail sales and household spending data could influence a potential rate cut at the RBA’s July 8 meeting. Job vacancies rose 2.9% in the three months to May 2025, a significant improvement from the prior quarter’s -4.3%, though they remain 28.5% below their May 2022 peak, signaling cautious optimism in the labor market. | ||
| Suggested reading | ||
| The Stock Market’s Irrational Exuberance, D. Lachman, AEIdeas (June 23, 2025) Being Human Means Being a Bad Investor, J. Wiggins, Behavioral Investment (June 24, 2025) | ||


